How to Use Excel MONTH Function?
Excel MONTH Function returns month as a number or numerical values between 1-12 from a given input date.
TL;DR
The MONTH function extracts the month as a number (1–12) from a given input date. For example, it returns 1 for January, 6 for June, and 12 for December. The syntax of the MONTH function is =MONTH(date). For instance, the formula =MONTH("23-July-2022") returns 7 as the output. The MONTH function returns a #VALUE! error if the input is not a valid Excel date. It will return a #NUM! error if the input number exceeds the range of valid Excel dates.Find more helpful Excel tips on our homepage: Excel24x7.com.
MONTH Function: A Brief
The MONTH function in Excel is used to extract the month number (1 to 12) from a given input date. The MONTH function will return a #VALUE! error if the input is not a valid Excel date. It will return a #NUM! error if the input number is outside the acceptable range for Excel date values.
| Objective | Value Returned by function |
|---|---|
| Aim to return a valid month as number | MONTH Function will extract the month from the given input date and return the month number as the numerical value lies between 1-12! |
MONTH Function: A Syntax
=MONTH(date)- date: This is the date from which you want to extract the month. It can be a cell reference containing a date, or a date written directly inside the formula using the DATE function.
This MONTH Function was introduced in the Excel 2003 version.
Basic Example of using MONTH Function:
In the below example, I’ve covered most of the common ways to use the MONTH function are shown using different types of input values.
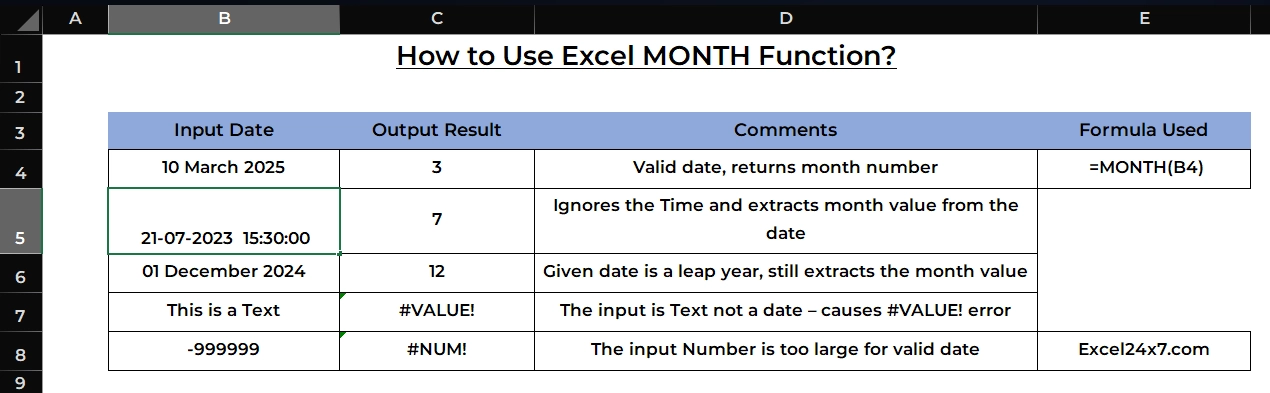
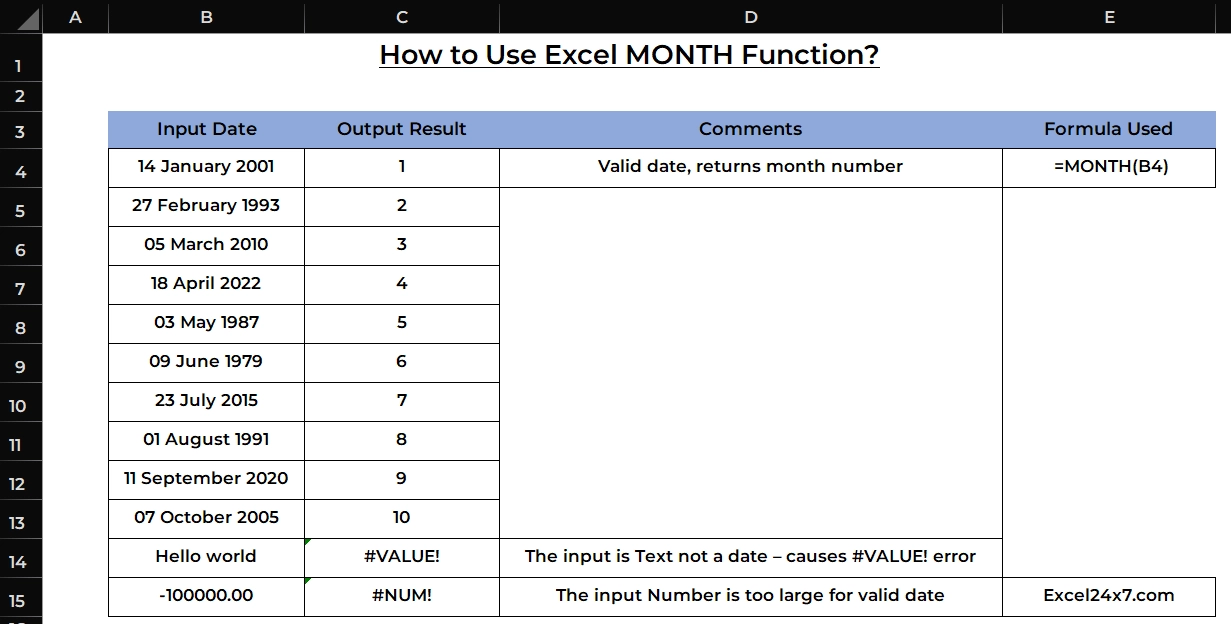
| Formula Used | =MONTH(B4) |
| S.no | Input Date | Output Result | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 March 2025 | 3 | Valid date, returns month number |
| 2 | 21 July 2023 | 7 | Ignores the Time and extracts month value from the date |
| 3 | 01 December 2024 | 12 | Given date is a leap year, still extracts the month value |
| 4 | This is a Text | #VALUE! | The input is Text not a date – causes #VALUE! error |
| 5 | -999999 | #NUM! | The input Number is too large for valid date |
Example Explanation:
- First example: The function extracts the month number from a valid date. March is the 3rd month, so it returns numerical value 3.
- Second example: Even if the input includes a time, the MONTH function looks only at the date part. Since the date is in July, it returns 7.
- Third example: The input date falls in a leap year, but this does not affect how the month is extracted. Since it’s December, the function returns 12.
- Fourth example: The input is plain text that does not follow a valid date format. So, the MONTH function returns a #VALUE! error.
- Fifth example: The input is a negative number too low to be a valid Excel date. In this case, the MONTH function returns a #NUM! error.
Using MONTH Function with other Nested Functions:
The following examples explains, how can we use the MONTH function with other Excel functions for multiple scenarios.
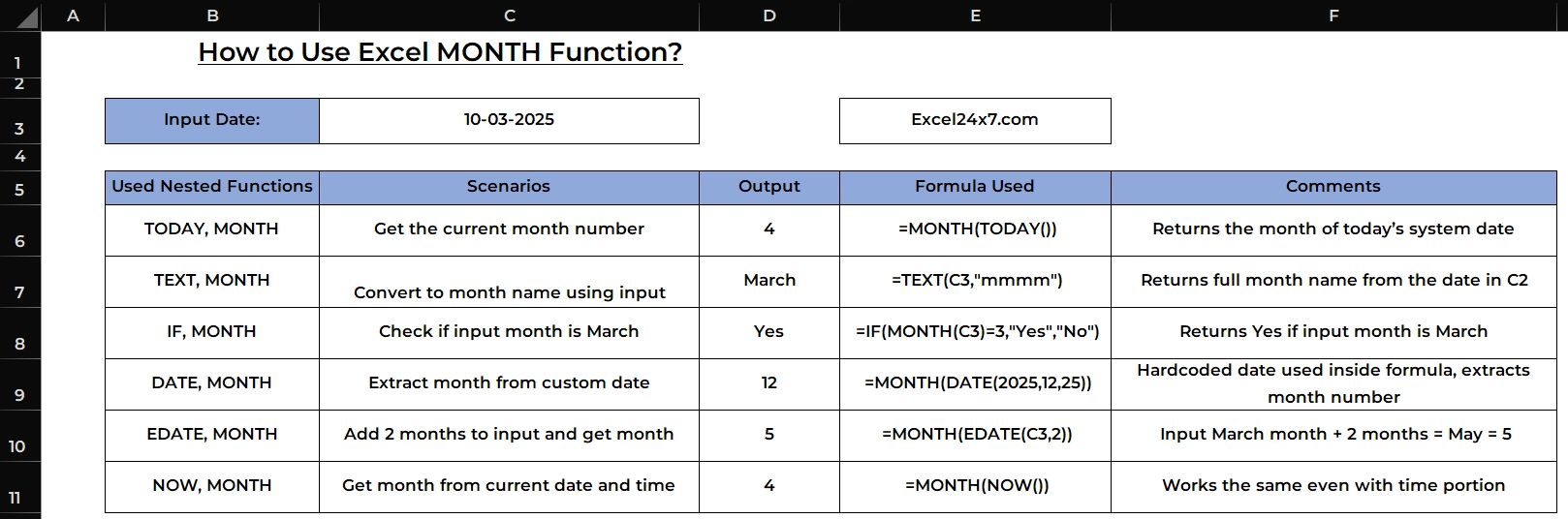
| Input Date | 10-03-2025 |
| S.no | Used Nested Functions | Scenarios | Output | Formula Used | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TODAY, MONTH | Get the current month number | 4 | =MONTH(TODAY()) | Returns the month of today’s system date |
| 2 | TEXT, MONTH | Convert to month name using input | March | =TEXT(C3,”mmmm”) | Returns full month name from the date in C2 |
| 3 | IF, MONTH | Check if input month is March | Yes | =IF(MONTH(C3)=3,”Yes”,”No”) | Returns Yes if input month is March |
| 4 | DATE, MONTH | Extract month from custom date | 12 | =MONTH(DATE(2025,12,25)) | Hardcoded date used inside formula, extracts month number |
| 5 | EDATE, MONTH | Add 2 months to input and get month | 5 | =MONTH(EDATE(C3,2)) | Input March month + 2 months = May = 5 |
| 6 | NOW, MONTH | Get month from current date and time | 4 | =MONTH(NOW()) | Works the same even with time portion |
Example Explanations:
- First one:
- This formula uses TODAY() inside MONTH() to return the current month number based on your system’s date. Since TODAY() always fetches the present date, MONTH(TODAY()) gives you the month part of that date.
- Second one:
- The TEXT() function is used here with a date cell to convert the date into a full month name like “March“. It doesn’t return the month number, but a readable month name, which is useful for headings or summaries.
- Third one:
- This formula checks if the month in cell C3 is equal to 3 (March). If true, it returns “Yes”, otherwise it shows “No”. This is useful for setting up conditions based on specific months in your data.
- Fourth one:
- Using the DATE() function, this formula creates a specific date, December 25, 2025. Then, MONTH() extracts the month part from that date, returning 12 for December.
- Fifth one:
- The EDATE() function moves the given date forward by 2 months. If the original date is in March (month 3), adding 2 months brings it to May (month 5), which MONTH() then returns.
- Sixth one:
- The NOW() function gives the current date and time. Even though the time is included, MONTH(NOW()) will still extract only the month number from the full timestamp.
That’s it.
Feel free to comment us below, if you have any queries about the above topic and find more interesting excel tutorials on our homepage: Excel24x7.com.
References:
- MONTH Function by Microsoft Support, Retrieved on 18/04/2025: Link.
- A Complete Guide on How to Use the Excel Month Formula by Indeed Editorial, Retrieved on 18/04/2025: Link.
- MONTH by Google Support Hub, Retrieved on 18/04/2025: Link.
- Excel MONTH Function – extract the month from a date | Excel One Minute Quick Reference by Chris Menard, Retrieved on 18/04/2025: Link.
- How to Use the MONTH Function in Excel in Just 3 Minutes ⏱️by Productivity Land, Retrieved on 18/04/2025: Link.
- How to Use MONTH Function in Excel by Excel 10 tutorial, Retrieved on 18/04/2025: Link.